Linux(四) 使用结构化命令 |
您所在的位置:网站首页 › 嵌套if else语句的特点和使用注意事项 › Linux(四) 使用结构化命令 |
Linux(四) 使用结构化命令
|
if-then
if command
then
commands
fi
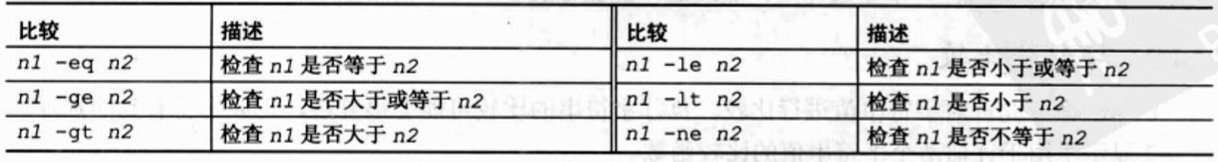
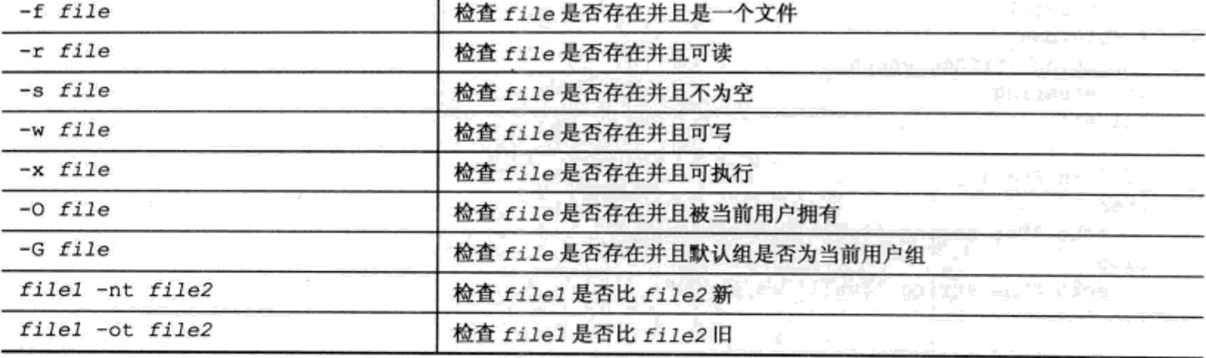
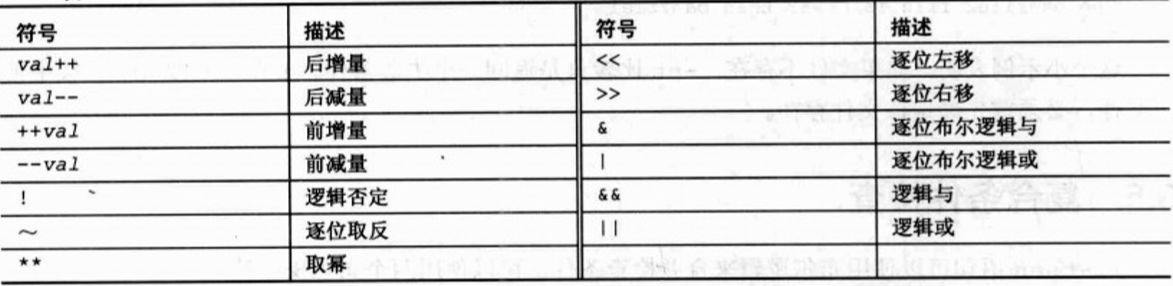
bash shell中的if语句运行在if行定义的命令. 如果命令突出状态时0, 将执行then后面的命令. 如果命令的退出状态时0以外的其他值,那么then后面的命令将不会执行.#!/bin/bash # testing the if statement if date echo "it worked" fiecho "we're outside of the if statement" # 输出: it worked ; we're outside of the if statementif语句行使用 grep 命令搜索/etc/passwd文件,查看系统是否正在使用一个特定的用户名.如果一个用户拥有该登录名,脚本会显示一些文本,然后列出用户HOME目录下的bash文件. 如果变量testuser设置成系统中不存在的一个用户,什么都不会列出 #!/bin/bash # testing multiple commands in the then section testuser=root if grep $testuser /etc/passwd then echo The bash file for user $testuser are: ls -a /home/testuser/.b* fi if-then-else if command then commandselse commands fi如果 if 语句行的命令返回的状态码为0, 就会执行在 then 部分列出的命令, 就像在普通的 if-then 语句中一样.如果if语句行的命令返回非零退出状态码,bash shell 将会执行 else 部分的命令 #!/bin/bash # testing the else sectiontestuser=badtestif grep $testuser /etc/passwdthen echo The files for user $testuser are: ls -a /home/$testuser/.b*else echo "The user name $testuser doesn't exxist on this system"fi输出: The user name badtest doesn't exist on this system 嵌套 if 语句 if command1then commed2elif commed2then more commandselif commed3then more commandsfielif语句行提供另一条要评估的命令,与原始的if语句行相似. 如果elif命令返回的退出状态码为 0, bash 执行第二个then语句部分的命令 命令块的执行依赖于哪条命令返回的退出状态码为0. bash shell 会按顺序执行 if 语句, 只有第一个返回0退出状态的命令会导致then部分命令被执行. test提供一种检测 if-then 语句中不同条件的方法. 如果 test 命令中列出的条件评估值为 true, test 命令以0 退出状态码退出, 这使 if-then语句使用与其他编程语言中的 if-then 语句一样的方法运行. 如果条件为 false, 则 test 命令退出, 使得 if-then语句失败 test condition # condition是一系列test命令评估的参数和值. 在if-then语句中使用时, test命令如下所示 if test condition then commands fi # bash shell 提供一种在 if-then 语句中声明 test 命令的另一种方法: if [ condition ] then commands fi # 方括号定义在test命令中使用的条件. # 注意, 在前半个方括号的后面和后半个方括号的前面必须都有一个空格,否则会得到错误信息 # test命令能评估一下3类条件: 1.数值比较, 2.字符串比较, 3.文件比较1) 数值比较 # -----------------------------------------------------------------------#!/bin/bash# testing floating point numbersval1=` echo "scale=4; 10 / 3 " | bc`echo "The test value is $val1"if [ $val1 -gt 3 ]then echo "The result is larger than 3"fi # 输出: The test value is 3.333 ; [: 3.333: integer expression expected 当使用 bash 计算器来生成一个浮点值, 并将它存储在变量 val1 中, bash shell 将无法处理成功. bash shell 只能处理整数数字, 在面向数值函数(如数值测试条件)中不起作用. 2) 字符串比较 警告: 空变量和没有初始化的变量可能会对shell脚本测试产生灾难性的影响.如果不确定变量的内容, 在数值比较或者字符串比较中使用它之前, 最好使用 -n 后者 -z 测试一下它是否有值 3) 文件比较 test命令能够测试Linux文件系统上的文件状态和路径 3.1 检查目录 [ -d ] -d 测试检查指定的文件是否作为目录存在于系统中 #/!bin/bash # look before you leap if [ -d $HOME ] then echo "Your HOME directory exists" cd $HOME ls -a else echo "There's a problem with your HOME directory" fi3.2 检查对象是否存在 [ -e ] #!/bin/bash # checking if a directory exists if [ -e $HOME ] then echo "OK on the directory, now let's check the file" # checking if a file exists if [ -e $HOME/testing ] then # the file exists, append data to it echo "Appending date to existing file" date >> $HOME/testing else # the file doesn't exist, create a new file echo "Creating new file" date > $HOME/testing fi else echo "Sorry, you don't have a HOME directory" fi3.3 检查文件 [ -f ] #!/bin/bash # check if a file if [ -e $HOME ] then echo "The object exists, is it a file?" if [ -f $HOME ] then echo "Yes, it's a file!" else echo "No, it's not a file!" if [ -f $HOME/.bash_history ] then echo ".bash_history is a file!" fi fi else echo "Sorry, the object doesn't exist" fi3.4 是否能读 [ -r ] #!/bin/bash #testing if you can read a file pwfile=/etc/shadow #first, test if the file exists, and is a file if [ -f $pwfile ] then # now test if you can read it if [ -r $pwfile ] then tail $pwfile else echo "Sorry, I'm nuable to read the $pwfile file" fi else echo "Sorry, the file $file doesn't exist" fi3.5 检查空文件 [ -s ] #!/bin/bash # testing if a file is empty file=t15test touch $file if [ -s $file ] then echo "The $file file exists and has data in it" else echo "The $file exists and is empty" fi date > $file if [ -s $file ] then echo "The $file file has data in it" else echo "The $file is still empty" fi3.6 检查是否能够向文件中写入数据 [ -w ] #!/bin/bash # checking if a file is writeable logfile=$HOME/t16test touch $logfile chmod u-w $logfile now=`date +%Y%d-%H%M` if [ -w $logfile ] then echo "The program ran at: $now" > $logfile echo "The fist attempt succeeded" else echo "The first attempt failed" fi chmod u+w $logfile if [ -w $logfile ] then echo "The program ran at: $now" > $logfile echo "The second attempt succeeded" else echo "The second attempt failed" fi3.7 检查是否能够运行文件 [ -x ] #!/bin/bash # testing file execution if [ -x test16 ] then echo "You can run the script:" ./test16 else echo "Sorry, you are unable to execute the script" fi3.8 检查所有权 [ -O ] (大写字母O) #!/bin/bash # check file ownsership if [ -O /etc/passwd ] then echo "You're the owner of the /etc/passwdd file" else echo "Sorry, you're not the owner of the /etc/passwd file" fi# -G 比较检查文件的默认组, 如果它与用户的默认组相匹配,它就成功. 只检查默认组,而不检查用户的所有组 3.9 检查文件日期 [ -nt / -ot ] (更新 / 更旧) #!/bin/bash #testing file dates if [ ./test19 -nt ./test18 ] then echo "The test19 file is newer than test18" else echo "The test18 file is newer than test19" fi if [ ./test17 -ot ./test19 ] then echo "The test17 file is older than the test19 file" fi# 如果比较的文件不存在, 只返回一个失败条件 复合条件检查if-hen语句可以使用布尔逻辑来合并检查条件, 可以 使用两个布尔操作符: [ condition1 ] && [ condition2 ] [ condition1 ] ||| [ condition2 ] # 第一个布尔操作使用 AND 布尔操作符来合并两个条件,两个条件必须都满足才能执行then部分 # 第二个布尔操作使用OR布尔操作符来合并两个条件.如果任意一个条件评估为 true ,name就会执行 then 部分. #!/bin/bash # testing compound comparisons if [ -d $HOME ] && [ -w $HOME/test_sh/testing ] then echo "The file exists and you can write to it" else echo "I can't write to the file" fi if-then的高级特征 ( 双圆括号表示数学表达数 / 双方括号表示高级字符串处理函数 )1) 使用双圆括号 双圆括号命令允许在比较中包含高级数学公式. test 命令只允许在比较总进行简单的算数操作. 双圆括号命令提供更多的数学符号,这些符号是其他语言程序员习惯使用的符号. 双圆括号命令的格式是: (( expression )) 术语 expression 可以是任何的数学赋值表达式或数学比较表达式. 除了 test 命令使用的标准数学操作符,下图显示了在双括号命令中可以使用的其他操作符列表 可以在if语句中使用双圆括号命令,也可以使用普通命令在脚本总进行赋值 #!/bin/bash # using double parenthesis val1=10 if (( $val1 ** 2 > 90 )) then (( val2 = $val1 ** 2 )) echo "The square of $val1 is $val2" fi# 在双圆括号内的表达式中,不必转义大于号. 这是双圆括号提供的另一个高级功能 2) 双拥双方括号 双方括号命令为字符串比较提供高级功能. 双方括号命令的格式是: [[ expression ]] 双方括号包围的 expression 使用在 test 命令中使用的标准字符串比较. 但是它提供了 test 命令没有的另一个功能, 即模式匹配. 在模式匹配中,可以定义与字符串相匹配的正则表达式 #!/bin/bash # using pattern matching if [[ $USER == r* ]] then echo "Hello $USER" else echo "Sorry, I don't know you" fi casecase命令将制定的变量与不同的模式进行比较.如果变量与模式匹配, shell 执行为该模式制定的命令. 可以在一行中列出多个模式, 使用竖条操作符将每个模式分开. 星号是与任何列出的模式都不匹配的所有值. #!/bin/bash # using the case command case $USER in rich | barbara) echo "Welcome, $USER" echo "Please enjoy your visit";; testing) echo "Special testing account";; jessica) echo "Don't forget to log off when you're done";; *) echo "Sorry, you're not allowed here";; esaccase命令提供了一种为每个可能的变量值制定不同选项的更清楚的方法 小结: 结构化命令允许改变 shell 脚本中的普通执行流. 最基本的结构化命令是 if-then 语句.该语句允许评估一条命令, 并给予评估命令的结果执行其他命令. 如果执行的命令也失败了,可以扩展if-then语句以包含bash shelll 执行的一组命令. 只有当被估计的命令返回非零退出状态码时, if-then-else 语句才允许执行命令. 也可以使用elif语句将if-then-else语句连接起来. elif 与使用 else if 语句等同, 如果被估计的原始命令失败,可以提供额外的检查. 在大多数脚本中, 不是想估计一条命令, 而是想估计一个条件, 列如数值`字符串的内容, 或者文件或目录的状态. test 命令提供评估所有这些条件的一种简单的方法.如果条件评估为 true, test 命令就为 if-then 语句生成一个零退出状态码. 如果条件评估为 false, test 命令会为 if--then 语句生成一个非零退出状态代码. 方括号是一个特殊的bash命令,他是test命令的同义词.在if-then语句中可以使用方括号包围测试条件, 来检查数字, 字符串和文件条件. 双圆括号命令允许使用附加操作符执行高级数学评估, 双方括号允许执行高级字符串模式匹配评估. case命令,执行多条 if-then-else 命令并在列表中检查单个变量值的快速方法 |
【本文地址】
今日新闻 |
点击排行 |
|
推荐新闻 |
图片新闻 |
|
专题文章 |